It is essential to get accurate results when using manual focus so the image looks sharp and clear. You could spin the focus ring endlessly, but if you want to speed up your manual focusing, you can turn on focus peaking. But what exactly is focus peaking? What benefits does it offer, and is it something worth using? Let’s explore how to use it.
What is focus peaking?
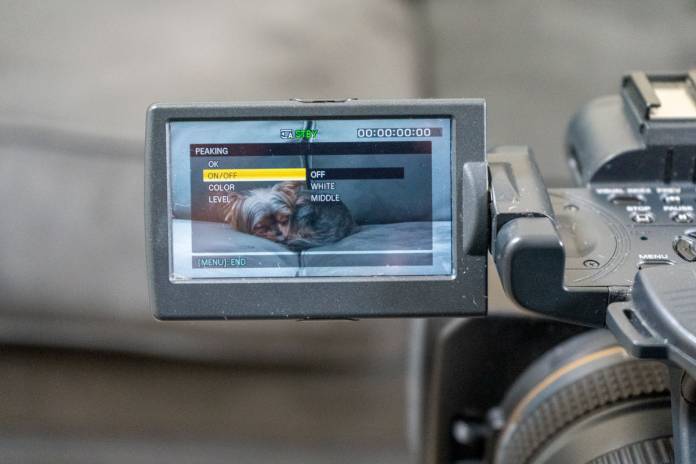
Focus peaking is a manual focus assistant that helps you focus more accurately. It works in real-time, highlighting sharp areas with a contrasting overlay. With focus peaking activated, you will be able to see what part of the image is in focus before shooting. To enable the feature, go to the camera menu and look for “Peaking Settings.” Usually, you will see three options; Display (On/Off), Level and Color. Let’s discuss each setting to understand better what they do.
Display (On/Off)
This option will turn on/off the peaking options. The picking option is most likely buried deep in the menu. We encourage you to program a button to turn on and off quickly. Assigning a button will be especially useful when using autofocus and manual focus at the same time.
Color

The highlighted sharp areas show up in a bright, contrasting color. You can select the color that fits best for the situation. The color selection varies by camera model, but you can expect white, red, yellow or blue. The critical part here is there’s no one-color-fits-all solution. You may have to switch colors on occasion depending on the dominant colors in your scene. For example, in the example below, the highlights are white, but they are a little challenging to see (take a closer look at the Yorkie right ear). In this situation, either the color red or yellow will work better.
Level

The level setting determines how much is highlighted. Most cameras have a high, middle and low. A high level will highlight more, and the lines will be bolder. A low level will highlight the sharpest areas of the photos, and the lines will be more challenging to see. The middle is a happy medium between low and high levels. Depending on the situation, select the appropriate level, but choose a high level for the most visible overlay.
Is focus peaking available in all cameras?
Initially, videographers used focus peaking with video cameras, so you may see older DSLR cameras or consumer cameras without that feature. Today, new mirrorless cameras come in with a focus peaking function. There are ways to enable it on some older models For example, it may be called Focus Assist for Live View. Check your camera manual to see if you have that option available.
When is it useful?
Since focus peaking works exclusively in manual focus, it is ideal for scenes where it is difficult to determine what is in focus. Here are a few scenarios where the feature is helpful:
- Shooting in low light conditions
- When your naked eye is having a tough time figuring out what is in focus
- When there are a lot of fine details, such as flowers, tree leaves, etc.
How to use focus peaking
Indeed, focus peaking can significantly impact your films or videos if you use it to accomplish your desired depth of field. To use it, set the focus peaking to high and manual focus on the subject until it is highlighted with the color overlay. In the example below, the Yorkie is highlighted in yellow while the lamp is not, meaning that the dog is focused.

The following scenario is the other way around. The Yorkie is out of focus while the lamp is in focus (highlighted in yellow). You can also notice that part of the sofa is highlighted too, which is also in focus.

Here’s how it looks in the viewfinder when you move the focus ring:
The end results:


The precise effect of aperture
Another great thing about using focus peaking is that it can help you determine if you might be using too wide an aperture. If you want everything to be in focus, you should start testing different apertures until you notice the viewfinder is highlighted fully with the color you selected. You may see that a higher aperture is not necessarily needed to get things in focus. Using focus peaking to confirm how your aperture selection impacts your shot will give you more control over your images. With its help, you will be able to achieve more subtle and powerful results.
When NOT to use focus peaking
As you can see, using focus peaking can get you to accomplish the depth of field easily. However, if you have a lens with an incredibly shallow depth of field (f/1.2), focus peaking highlights can obscure too much in the scene, preventing you from seeing details.
Another situation when focus peaking is not helpful is when it distracts you from the composition. Seeing color highlights all over the viewfinder can be offputting. Although the picture is in focus, it doesn’t necessarily mean it will look good. In this case, it is recommended to use focus peaking to get the desired focus, turn it off, and adjust composition accordingly. Evaluate the scene for exciting lights, colors and contrasts without the focus peaking covering up key elements.
Be aware that focus peaking is not perfect, so you may not want to rely entirely on focus peaking to focus your shots.
Focus peaking and autofocus at the same time
One excellent way to use focus peaking is when you combine it with autofocus (using direct manual focus, or DMF). You set up your camera to manual focus with focus peaking ON (make sure to assign it to a button) and use the autofocus button. When you are in a situation when you are constantly on the move, you press the autofocus button to get most things in focus, then you refine details manually using the feature.
Since you assigned focus peaking to a button, turning it On/Off will be easy. If you are using a DSLR camera, it is strongly recommended that you use the back button focus instead of the shutter. The focus peaking and autofocus combination are primarily helpful for recording videos such as weddings or low-light events.
Using a field monitor
A field monitor is an external, portable, battery-powered display that replicates the picture being recorded to the camera. You can attach them directly to your camera to get more accurate visuals. Most monitors include focus peaking, allowing you to ensure your recordings are always in focus.
Peaking practice!
Getting the most out of focus speaking takes practice. Although it is not a perfect manual focusing tool, he can be helpful in many situations. So go ahead and try out focus peaking. Have fun!